Laser Cutter Speed vs. Power: The Key Differences

A laser cutter uses an intense beam of monochromatic light to cut through a material. Finding the right cutting speed and cutting power can be challenging especially when there are so many variables. Variables include: material type, material thickness, and laser type. The way to find the optimal cutting speed and power are to use a laser cutting chart to identify the recommended cutting speed and then run a test on some scrap material to test for the right speed and power setting.
What Is Laser Cutter Speed?
Laser cutting speed is the rate at which the cutting of material occurs when using a laser. This rate is expressed in length per unit time; for example, inches/minute or millimeters/second. The cutting speed changes with variables including: material type, material thickness, the width of the cut, and laser power. As the material thickness or cutting width increases, or the laser power decreases, the cutting speed will slow down. Materials with a higher thermal conductivity will require more power to cut than materials that are less thermally conductive. This is because highly thermally conductive materials will dissipate heat quicker which prevents cutting from occurring.
What Is the Importance of Speed in Laser Cutting?
Speed is one of the most important variables in using a laser cutter. This is because a cutting speed that is too high may result in the laser not cutting the full thickness of the material. Conversely, if the cutting speed is too slow, then the laser will burn the edges of the cut, resulting in a poor finish. Slower cutting speed will also result in a drop in productivity which is important in a business application. For more information, see our guide on What is a Laser Cutter.
How To Identify the Laser Cutter Speed?
To correctly identify the right laser cutter speed, you must first use a chart to find the recommended laser cutting speed for the material type and thickness, as well as for the right laser type. Then, run a test on a scrap piece of material of the same type and thickness. Create 11 squares to be cut and set the speed to increase for each cut—where the middle square is the recommended cutting speed. Run the test and identify which squares are both completely cut and without burnt edges. There will be a range of speeds that produces an acceptable cut.
Is a Laser Cutter Speed Chart Helpful?
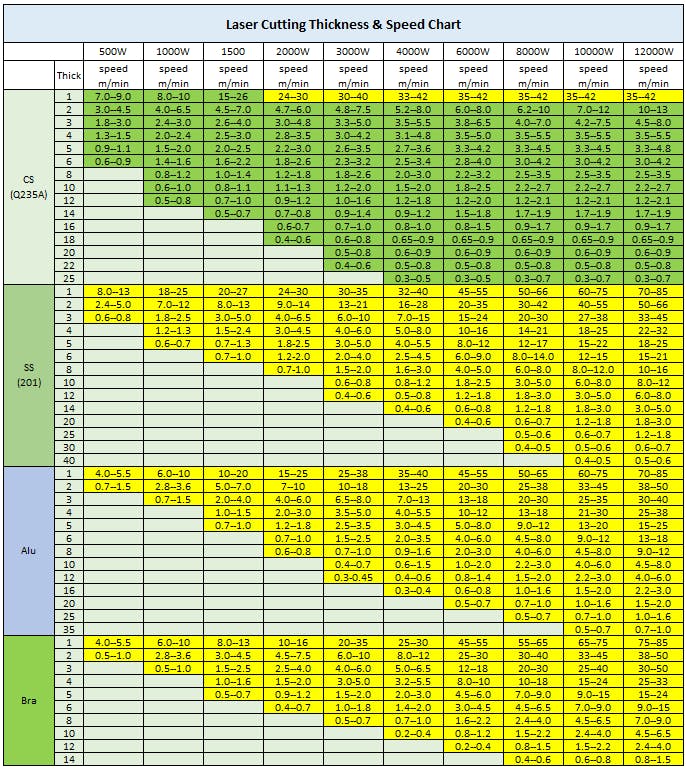
Yes, a laser cutter speed chart is helpful. If a chart is not used, then it could take an excess of time and a lot of material for a trial and error method to identify the right cutting speed. Using a chart rather than trying to calculate the cutting speed can save time in setting up the right cutting speed for the chosen material and thickness. Figure 1 below is a chart that shows the recommended cutting speeds for stainless steel 201, aluminum, and brass:
Laser cutter speed chart.
Image Credit: https://www.machinemfg.com/laser-cutting-thickness-speed-chart/
What Is the Speed Setting for Laser Cutting Wood?
When cutting 1/10” thick plywood with a 10 W diode laser, the recommended speed setting is 15.7 ipm. This is the recommended speed setting from a laser cutting chart for wood, and the speed that should always be tested first. Additionally, cutting wood that is thicker, denser, or with a lower-power laser will decrease this speed and vice versa.
What Is the Speed Setting for Laser Cutting Metal?
When cutting 1/10” thick aluminum with a 200 W CO2 laser, the recommended speed setting is 59 ipm. This recommended setting should be tested on a scrap piece of metal first to identify the optimal cutting speed. When cutting metals with high thermal conductivity, increased thickness, or a less powerful laser, then the cutting speed should be decreased.
What Is Laser Cutter Power?
The laser cutter power is the amount of light energy delivered by a laser per unit time. This should not be confused with power density which is the amount of power per unit area. The greater power the faster the laser can cut or the laser can cut thicker material.
What Is the Importance of Power in Laser Cutting?
The power setting is an important variable in laser cutting as the power will affect the speed and depth that the laser cutter can cut. In addition, if the laser is too powerful it may cut the material but will locally char the cut edge.
How To Identify the Laser Cutter Power?
Identifying the laser cutter's power will require knowing the laser cutter's speed and material type and thickness. To start, a laser cutting power chart should be used to find the recommended power required for the given thickness, material type, and cutting speed. Create 11 squares to be cut and set the power to increase for each cut—where the middle square is the recommended cutting power. Run the test and identify which squares are both completely cut and without burnt edges. There will be a range of powers that produce an acceptable cut.
Is a Laser Cutter Power Helpful Chart?
Yes, a laser cutter power chart can be helpful. Charts can help quickly select the right power setting for the required application. However, it is always best to run a test on some scrap material to work out if the power on the chart is the right power.
What Is the Power Setting for Laser Cutting Wood?
When laser cutting wood 150 W–800 W, CO2 lasers are the best choice. These powerful lasers can cut through wood up to 3⁄4'' thick. The exact power setting will depend on the wood type and thickness. Generally, the thicker the cut the higher the power setting. Additionally, the harder the wood the more power is required.
What Is the Power Setting for Laser Cutting Metal?
The power required to cut metals is much higher than for cutting wood at >1 kW for CO2 lasers. The material type and thickness will dictate the exact power setting. The thicker the metal, the more power is required. Additionally, the more thermally conductive the metal, the more power is required. It is best practice to find an approximate cutting power using a chart, and then run a test using scrap metal of the same thickness.
How Do Laser Cutter Power and Speed Impact Cutting?
The power and speed of laser cutting will impact the cut finish. Additionally, the speed of cutting will affect the productivity of the machine, which is important in a business application. Higher-power laser cutters allow for faster cutting speeds; this applies up until the edge of the material starts to char. The speed of the cutting will affect the contact time of the laser with the cut. An increase in speed may lead to the material not being cut, a decrease may lead to the laser burning the material's cut edge.
Does Increasing Laser Cutting Speed Improve Quality?
No, increasing the laser cutting speed does not improve quality. The only exception is if the laser cutter is moving too slowly and burning the edges of the cut. However, if the laser cutter is moving at an appropriate speed, then increasing the speed will likely result in the laser cutter ceasing to cut effectively.
Does Adjusting the Laser Cutting Speed Impact the Accuracy of the Cut?
No, the speed of the laser cutting does not impact the accuracy of the cut. Higher speed means the laser cutting is faster, resulting in a lower energy exposure, which could lead to the cut being too shallow and/or smoke and charred edges. Similarly, a lower speed results in slower cutting and therefore a deeper cut.
Does Laser Cutting Speed and Power Depend on the Thickness of Materials?
Yes, the type of the material and its thickness primarily determine the speed and power of the laser cutter. Where there is a fixed laser power, the thicker the material, the slower the cutting speed will be, therefore implying that speed and laser cutting thickness are inversely proportional.
What Speed and Power for Acrylic Laser Cutting?
When cutting acrylic ⅙” with a 5.6 W diode laser, a cutting speed of 6 ipm is recommended. However, if the thickness is increased, or the power is decreased, then the speed would need to be slower to effectively cut the acrylic and vice versa. For more information, see our guide on Acrylic Cutting.
Is It Hard To Set the Perfect Laser Cutter Speed and Power Setting?
Yes, finding the right cutting speed and power setting is difficult. To find the right parameters for laser cutting, a chart with predetermined settings should be used. Then, a test should be conducted on a scrap piece of material of the same material type and thickness to identify which speed and power create the optimal cut.
Are Speed and Power Setting Significant in Laser Engraving?
Yes, the speed and power settings are significant in laser engraving. In laser engraving, the top surface layers of the materials are melted away by a laser beam to create a specific design. If the laser speed is too quick, the cut might not be deep enough and therefore the design is not clear. Alternatively, if the speed is not quick enough, the laser will be concentrated in one place for too long which could burn the material. To learn more, see our guide on What is Laser Engraving.
Summary
This article presented laser cutter speed vs. power, explained both of them, and discussed their key differences. To learn more about laser cutting, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including sheet cutting and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.